
Arquivo para a ‘Método e Verdade Científica’ Categoria
Idealism and real experience
The great discovery of real life (or rediscovery if we take classical and medieval ontology as a basis) is a radical critique of idealism, which separates the subject of life from the real world, what is promised in life projected onto things and not things (our posts from last week) is the real-life catastrophe that does not translate into real and concrete values.
we take classical and medieval ontology as a basis) is a radical critique of idealism, which separates the subject of life from the real world, what is promised in life projected onto things and not things (our posts from last week) is the real-life catastrophe that does not translate into real and concrete values.
Phenomenology returns to real life through the Lebenswelt (world of life) that was taken up by the philosopher Husserl and that is touched upon and cited by Habermas, without really developing it.
The objective of this philosophy is to show that the human being must be the center of the knowledge process, human consciousness is a giver of meaning to the world of things, or the phenomena of this world, from which the name phenomenology comes, non-things can also reacquire meaning if we penetrate this human reason (which idealism calls subjectivity).
With this, human consciousness reacquires meaning and meaning to phenomena and things in the world, directing them to what each thing is in essence, in a path that is always intentional and thus gives meaning.
Husserl in his work “Crisis of European Sciences and Transcendental Phenomenology”, is where this concept appears in a clear and in-depth way, because it establishes a relationship between epistemology (the systematization of knowledge) and philosophy and rediscovers asceticism.
Thus, a true asceticism does not separate the world of things and non-things, just showing that there would be an unreality in one of these worlds, as it is not separated from life, it is there that we verify that we move from the concrete world of life to a path whose evolution destroys the basis of the human and the real, wars and personal declines are this.
In Habermas the world of life is treated as something that is immediately available to social actors in the form of meaning and/or representations available to everyone, whereas for Husserl the phenomenological foundation refers to an ethics for the science and technique of the world, given that science has not managed to reach this level as a discourse on action in which the life of reflection is absent, and within science, which is what Kant’s criticism does.
Sloterdijk developed something close to this concept as a despiritualized asceticism, that is, despite working on the concept of “phenomenology of the spirit” they remain in the abstract field and their real updating in the world of life does not happen, because it is not clear what type of exercise this is.
So we carry out a series of “exercises”, we are the society of physical and mental exercises, but their translation into the world of life does not lead to concrete social and moral acts.
Husserl, Edmund. (1986). La crise des sciences européennes et la phénomènologie transcendentale. Trad. De Gerard Granel. Paris: Edittrice CLUEB.
The included third of physics and thought
The fact that we are trapped in dualism, A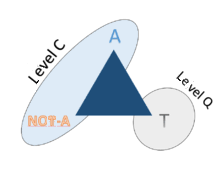 and not-A, Being is and Non-Being is not, and now transformed into political thought as if nature and society were just always two options in conflict with no third (or even the fourth and fifth options) is an outdated thought if we look at the logical paradox developed by the physicist Barsarab Nicolescu that finds parallels not only in quantum physics (photo), but also in social and ontological thinking: the third option.
and not-A, Being is and Non-Being is not, and now transformed into political thought as if nature and society were just always two options in conflict with no third (or even the fourth and fifth options) is an outdated thought if we look at the logical paradox developed by the physicist Barsarab Nicolescu that finds parallels not only in quantum physics (photo), but also in social and ontological thinking: the third option.
So much so that this is true that Barsarab’s own text that calls for a reform of Education and Thought (Barsarab, 1999) indicates that this change can be seen as a way out of the center of a crisis greater than physical or logical issues, says Barsarab : “One thing is certain: a large gap between the mentality of the actors and the internal development needs of a type of society invariably accompanies the fall of a civilization”, or said in another, more ontological way, between Being and non-being -Being there is a state of Non-Being that breaks dualisms and paradoxes.
Both Barsarab’s letter that calls for an education reform, and other thinkers such as Edgar Morin and others perceived a crisis in modernity with roots in thought and education, the theorist of the Included Third T, gives a worrying sentence: “The risk is enormous , because the continuous expansion of Western civilization, on a global scale, would make the fall of this civilization equivalent to the burning of the entire planet, in no way comparable to the first two world wars”.
There is also a linear and monodirectional thinking where intentionality is always polarized and creating a “single” and monochromatic path, with the eternal danger of authoritarianism and misuse of power, to detente it will be necessary to have a more open world where everyone is included and not just what is convenient for power.
Education must support and assist this context, Barsarab says in his letter: “The harmony between mentalities and knowledge presupposes that such knowledge is intelligible and understandable. But can this understanding still exist, in the era of the disciplinary big bang and extreme specialization?”
The harsh reality of the pandemic shows that we oscillate between true solidarity and detente to face the crisis, and the opportunist polarization that wants to take advantage of the deaths and deviations of a poorly managed health crisis, in some countries more, but in almost all .
Barsarab’s sentence, which seems harsh, is not: “Is there something between and across disciplines and beyond each and every discipline? From the point of view of classical thought there is nothing, absolutely nothing. The space in question is empty, completely empty, like the vacuum of classical physics”, in this epoché (the Greek vision of emptiness) a true philosophy can flourish, even when it is not (the suspension of judgment, new horizons beyond the pre -concepts, etc.) is what it is.
NICOLESCU, Basarab. The manifesto of transdisciplinarity. Trans. Lúcia Pereira de Souza. Brazil, São Paulo: Trion, 1999.
Bad taste is becoming common
The word is not mine, but none other than the northeastern brazilian writer Ariano Suassuna, in a talk that someone had the happy idea of turning into a short YouTube post, he adds: “the ability to be outraged by what It’s ugly, he said, I watch a soap opera, I think the soap opera is an important thing that we have to watch, a soap opera was on and it was actually good, but in the entrance music there’s a verse, notice what, my stone is amethyst, my color is the yellow one, but I’m honest I need to go to the scientist urgently”… the audience laughed… and he added: “be patient, this is too bad” (short talk with Ariano Suassuna).
northeastern brazilian writer Ariano Suassuna, in a talk that someone had the happy idea of turning into a short YouTube post, he adds: “the ability to be outraged by what It’s ugly, he said, I watch a soap opera, I think the soap opera is an important thing that we have to watch, a soap opera was on and it was actually good, but in the entrance music there’s a verse, notice what, my stone is amethyst, my color is the yellow one, but I’m honest I need to go to the scientist urgently”… the audience laughed… and he added: “be patient, this is too bad” (short talk with Ariano Suassuna).
Theodore Dalrymple, is the pseudonym of the English psychoanalyst Anthony Daniels, who decided to write essays and transformed 26 essays into a book Our Culture or what’s left of it, and now working as a volunteer in a work that re-educates addicts and understood more deeply what the author wanted to say, it’s not about sentimentality or simply giving the recipe: “society did this to him”, it’s partly true, but by their own decision these people can change their lives. (interview in Brazil)
The decision is individual and can change lives and realities, it is possible to give hope back to people who life has pushed aside, without using demagoguery or treating these people with prejudice, helping them to face their own reality head on, and then the social reality , but the decision is a first personal step.
The taste for the ugly, unethical and immoral is not a final option, it can be reversible, but the recipe for success is to face personal and social reality, without running away from its responsibilities and willing to see alternatives of education, respect and ethics that neither it’s always the takes.
Giving alms, a plate of food can be an immediate measure, but preventative measures require a change in perspective on life, of an often-complex metanoia that dismantles adopted antisocial values, and psychoanalyst Anthony Daniels speaks with authority, because he has dealt with many of these extreme cases in prisons and in his office.
He adopted the pseudonym probably to demonstrate that these are not just cases and psychic disorders, but addictions and antisocial attitudes that transform into destructive and negative thoughts and actions.
The first part of the book deals with arts and letters and the second part with society and politics, but the author does not fail to deal with the future in both parts, where we were going and are almost there: the downhill slope we entered and if It is possible to reverse this process.
In addition to criticizing the Eurocentric, idealistic way of thinking and the demand for efficiency, he, who is European, shows paths similar to those that seek to take people off the path of degradation.
Anyone who watches these influencers who offer rewards out there, basic questions, such as the first capital of Brazil, the capital of a state other than São Paulo or Rio Grande do Sul, the others seem unknown, math questions then border on ignorance.
Questions like how much is 10 to the power of 0 in mathematics, fruits that start with P (Pera (pear), Pitanga (typical in Brazil), Ponkan (type of tangerine), etc.), in short, very simple questions that few people answer.
Dalrymple, Theodore. “Our culture, what-s left of it”, ed. Ivan R. Dee Pub., Chicago, 2005.
Non-things and subjectivity, the distorted eidos
Subjectivity comes from idealism that judges Being separate from things, thus only being if projected onto objects, but the Greek “eidos”, from which nascent idealism came, there was no such separation, both in Aristotle’s 4 causes: material, formal, efficient and final, as well as in the theory of Platonic ideas, which is the essence and which we have already related to the thing.
separate from things, thus only being if projected onto objects, but the Greek “eidos”, from which nascent idealism came, there was no such separation, both in Aristotle’s 4 causes: material, formal, efficient and final, as well as in the theory of Platonic ideas, which is the essence and which we have already related to the thing.
Those who think the world is immersed in eroticization are mistaken, be it the world of fantasy, that which comes from works of fiction, from children’s imagination and from looking with hope at a better future, today in an increasingly worrying present, Chul- Han writes like this:
“Without fantasy, there is only pornography. Today, the perception itself has pornographic features. It occurs as an immediate contact, even as a copulation of image and eye. The erotic occurs in the blink of an eye” (Han, 2022), that is, it is precisely its opposite, we are in the existential void, in the denial of Being and in it only pornography remains, as a degradation of Being.
Quoting Barthes, Hul-Han clarifies the part of the piece that is: “Absolute subjectivity can only be achieved in a state of silence, the effort to achieve silence (closing the eyes means making the image speak in the silence). Photography touches me when I remove it from its usual blahblablah […] not say anything, close my eyes […]” (Han, 2022) and he is quoting Roland Barthes in his work (photo): The camera lucida (or Lucid, depending on the translation).
Photography is therefore a way of perpetuating silence, the desire of many to take photos as an individual act is to remove it from everyday life and insert something that is eternal, while the public exposure that the digital universe has allowed is to return it to the “ usual blahblabla”, says the author: “The disaster of digital communication arises from the fact that we don’t have time to close our eyes” and maybe he doesn’t know but this is even physical, by not blinking our eyes we should use eye lubricants if We expose it for a lot of time on screens.
“Noise is both acoustic pollution and visual pollution. It pollutes attention” (Han, 2022) and citing Michel Serres says that this instinct is of animal origin, as dogs, tigers and other animals that urinate to demarcate land, pollute with their stench to inhibit other animals from approaching.
Allowing others to approach is not demarcating territory. Jesus’ biblical response to the initial contact of two new disciples is wise (John 1:38): “Jesus asked: “What are you looking for?” They said, “Rabbi (which means: Master), where do you live?” and he replied: “Come and see” and they went and stayed with Him, because he did not demarcate ground and did not close himself.
The logic of silence is contrary to noise, which does not just mean the pollution of an audible sound, but a complete void capable of containing and receiving the Other.
Han, Byung-Chul (2022) Não-coisas : reviravoltas do mundo da vida , transl. of the Rafael Rodrigues Garcia. Brazil, Petrópolis, RJ: ed. Vozes.
The non-thing and the amoral world
For Byung Chul-Han, what is changing is the world of merchandise with the digital, he will analyze the power of the book and the ebook, the latter as a non-thing, the smartphone and other digital objects, but the world of morals as well is changing, he quotes in passing:
world of merchandise with the digital, he will analyze the power of the book and the ebook, the latter as a non-thing, the smartphone and other digital objects, but the world of morals as well is changing, he quotes in passing:
“A person uninterested in things, in possessions, does not submit to the “morality of things” based on work and property. She wants to play more than work; experience and enjoy more than possess. In its cultural phase, the economy also shows playful traits. Theatrics and performance are becoming increasingly meaningful. Cultural production, that is, the production of information, increasingly adapts artistic processes. Creativity becomes its motto”, using Vilém Flusser’s reasoning about the moral of the thing.
What Chul-Han calls the cultural phase should be an in-depth analysis of the period of the cultural industry, radio, cinema and television, which was nothing more than a transition from merchandise to the imagination through advertising, where the brand and not the content, so not only are the work and the product alienated, but its very essence is alienated, using a term from the medieval period, as we have already analyzed in a previous post, it loses its quiddity, its identity and singularity, as it was the cultural industry that gave everything the appearance of sameness.
Also in the final section he will analyze things of the heart, and it is good to remember that these also had their singularity in the past, today transformed into an amoral and timeless character, in the wrong sense of the word, what is eternal is essence and singular and then returns to quiddity.
The final section says, things of the heart, recalling the fox’s dialogue with The Little Prince by Antoine de Saint-Exupéry: “The little prince asks the fox what “apprivoiser” means. To which the fox responds: “It’s something almost forgotten […]. It means becoming familiar, establishing relationships. […] For me, you are just a little boy like a hundred thousand others” and this is the loss of singularity, there it will introduce listening and the relationship with the Furthermore, these relationships cannot be developed without a moral conception.
The exposure of personal relationships, the end of private life through legal and illegal filming, the increasing exposure of even children, is increasing and amoral, there is no room for growth and respect for the morals of each age, not even old age, Rejected as moral and as an age of wisdom, it is increasingly common to expose this “good age” in a pejorative and amoral sense, without limits of respect (Chul-Han calls it symmetry in The Swarm) and a balanced morality.
Everything seen as “freedom”, but which plunges into “upheavals in the world of life”, the author’s subtitle, we are heading towards a civilizational crisis and the return depends not on things, but on a new morality of the state, of human relations and of public life.
Han, Byung-Chul (2022) Não-coisas : reviravoltas do mundo da vida / Byung-Chul Han ; tradução de Rafael Rodrigues Garcia. Brazil, Petrópolis, RJ: ed. Vozes.
What are things
When rereading Byung Chul-Han’s “Non-Things”, he correctly recalls that the term comes from Vilém Flusser, who lived in Brazil for a good part of his life, and also takes up the concepts of Hanna Arendt and Heidegger, but does not penetrate in the essence of the thing, which is not just information.
he correctly recalls that the term comes from Vilém Flusser, who lived in Brazil for a good part of his life, and also takes up the concepts of Hanna Arendt and Heidegger, but does not penetrate in the essence of the thing, which is not just information.
Medieval philosophers had already developed the question of quiddity, which is neither an idea nor a concept, but something that sought to understand the essence of things, from the Latin, “quidditas” means “what is that” and was related to the idea of identity and uniqueness.
Thus, by transforming it into information, it does what Luhman did with the concept (remember that this author deals more with the issue of communication than the thing in itself), he says, quoted by Byung Chul-Han: “His cosmology is a cosmology not of being, but of contingency”, that is, something that has no essence, no identity or singularity and cannot “be”.
Clarifying that it is a particular way of seeing information, as a “transmitted thing”, and in this the author is right: “Information cannot be possessed as easily as things. Possession determines the paradigm of the thing. The world of information is not governed by possession, but by access” (Han, 2022), this is so true that the Portuguese dictionary in Brazil now has a new word which is “logar”, from the English, log “registration” in the sense of marking access to “information”, in Chul-Han’s sense.
Quoting Jeremy Rifkin, Han warns that the transition from possession to access is a paradigm shift that leads to drastic change in the world of life, subtitle of the book, he predicts a new type of human being: “access, therefore, ‘access’ are key terms of the nascent era (Han, 2022).
Jeremy Rifkin, the transition from ownership to access is a profound paradigm shift that leads to drastic changes in the lifeworld. He even predicts the emergence of a new type of human being: “Access, ‘logon’, ‘access’ are the key terms of the nascent era. […]
Regarding the modified identity of the medieval sense, the author says: “We produce ourselves on social media. The French expression se produire means to put oneself on the scene. We act out. We perform our identity” (Han, 2022), mind you: it produces in the media Media are means, the confusion with the idea of networks, not on purpose of course, destroys the third characteristic of the thing which is its singularity, not in this essay, but in others, the author remembers that everything in the world is characterized by sameness, everything it looks very the same.
This world of “non-possession” is differentiated by enjoying more than living, it makes the “idealization of things” a task, it is not uncommon to see in programs and on social media a large number of utopian and bizarre questions, such as, what it would be if you were an object, if you lived on another planet, etc. and this amuses the public of non-things.
Revolutionaries should not be alarmed, but quoting Walter Benjamim, Chul-Han writes: “the deepest relationship one can have with things”, this substantiality is not materialistic but rather a rational and “informational” relationship with things, information here in another sense.
Han, Byung-Chul (2022) Não-coisas : reviravoltas do mundo da vida / Byung-Chul Han ; tradução de Rafael Rodrigues Garcia. Brazil, Petrópolis, RJ: Vozes, 202
The mystery of black holes
The center of the Milky Way, the galaxy where our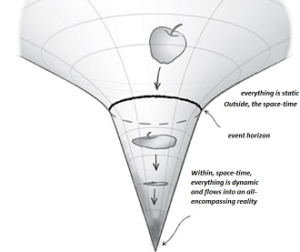 solar system inhabits, is formed by a disk with spiral arms and a dense, yellowish central region known as the “bulge” and there are around ten billion stars orbiting the colossal object that is its center called the supermassive black hole Sagittrius A*.
solar system inhabits, is formed by a disk with spiral arms and a dense, yellowish central region known as the “bulge” and there are around ten billion stars orbiting the colossal object that is its center called the supermassive black hole Sagittrius A*.
So, if in the past geocentrism (the Earth as the center) was a naive idea, now Heliocentrism (the sun as the center) is also a provincial and outdated idea, but what black holes are, it was not Einstein but Karl Schwarzschild who was the first to propose its existence.
Steven S. Gubser’s book “The Little Book of Black Holes”, deals in a simple way, as much as possible, explains Einstein’s special and general relativity and Schwarzschild’s equations that gave rise to the topic, black holes are one of the strong themes in current astronomy and one of the sources of research for the James Webb mega-telescope.
The book begins by recounting an experiment carried out on September 14, 2015, almost a hundred years after Einstein announced his theory of general relativity, two massive detectors, one in Louisiana and the other in Washington, were carrying out a gravitational wave experiment when they detected an audible signal, such as a serious knock and five months later they announced that they had detected two colliding black holes forming a larger one, the discovery was spectacular.
Both black holes and gravitational waves were predicted in Einstein’s Theory. In this theory, the black hole is a region of space-time (the notion of absolute time and space has already been overcome) where all nearby matter is attracted and is impossible to escape.
There is a popular saying that everything that goes up must come down, says the author, however the idea of the Schwarzschild equations is that nothing can go up, only come down and in the case of black holes where does that which must come down go, that is, what happens to what is attracted to the black hole.
We know the story of the apple that would have inspired Newton’s law of universal gravitation, the author of the book then suggests an apple falling into a black hole.
An apple outside the black hole events everything is static, at the horizon of these events everything is dynamic, flowing towards an all-encompassing singularity (where space-time changes dynamically in an extraordinary way, there two dimensions compress and the third is stretched.
Stephen Hawking, famous for proposing Big Bang equations, speculated that black holes are not actually black, they have their color (in fact, outside our visual range of colors from violet to red) determined by temperature, energy and entropy of its surface (if we can call the two dimensions that, since it is space-time).
This simplified introduction is developed over seven chapters of the book, in astronomical details and their equations, which requires some more specific knowledge of physics.
Gubser, Steven S., Pretorius, F. 2021. The Little Book of Black Hole. US: Princeton Press, 2018.
Physics and the mind of God
The basic original question of man is language, but when searching for information man was forced to look at the universe and try to understand its enigmas, geocentrism (the earth as the center of everything), heliocentrism (the sun as the center of everything) dominated human language and thought for millennia, throughout this time anthropocentrism dominated human conception and with this the attempt to dominate all of nature grew.
but when searching for information man was forced to look at the universe and try to understand its enigmas, geocentrism (the earth as the center of everything), heliocentrism (the sun as the center of everything) dominated human language and thought for millennia, throughout this time anthropocentrism dominated human conception and with this the attempt to dominate all of nature grew.
However, nature is indomitable, modernity was an attempt to dominate the forces of nature and assert anthropocentrism over it, but it has its own logic, and when looking more deeply the universe that had a mythological explanation moved to a more focused focus. clear of eschatological inquiry: where did we come from and where are we going.
The book by theoretical physicist Michio Kaku: “The God equation” takes a deep dive into this issue from contemporary physics and cosmology, the physicist is the great theorist of string physics (Hyperspace is one of his books), professor at Harvard and host of programs on Discovery Channel.
In his book he explains the quest of physicists such as Stephen Hawking and Albert Einstein to try to explain all the forces of the cosmos, what is called the theory of everything, and which in its current formulation is called the Standard Physics Theory, the discovery of quantum forces of particles, including the Higgs boson, the vision of the photon with a particle of zero mass, the particles of terrestrial magnetism helped this unification, but that’s not all.
Many physicists have failed, the quantum explanation breaks with the idea of “thing” that some dualist authors continue to have, the “quantum” is something beyond it has a third state, called in physics the “third included” where a particle is between the Being and Non-Being and is not dual.
If this state of quantum physics is already a reality, what the particles actually are is still a mystery, and the “most promising candidate (and, in my opinion, the only candidate) is string theory, which says that the universe it is not made of point particles, but rather of tiny vibrating strings, where each mode of vibration corresponds to a subatomic particle” (Kaku, 2022).
We would need a microscope powerful enough to see electrons, quarks, neutrinos, etc. they are nothing more than vibrations of tiny loops, similar to rubber bands. If we put these elastic bands to vibrate countless times and in different ways, we will eventually be able to create all the subatomic particles in the universe, and this means that the laws of physics are summarized in these modes of vibration of the small strings.
Kaku says in the introduction to his book: “chemistry is a set of melodies that we can play with them. The universe is a symphony. The mind of God, which Einstein eloquently referred to, is a cosmic music that spreads across space-time” (Kaku, 2022).
Kaku, Michio. 2022. A equação de Deus (The God equation). Trans. Alexandre Cherman, Brazil, R.J.: ed. Record, 2022.
Happy 2024 and blog line
It is difficult to make a positive assessment of 2023, we expected some positive reaction from humanity in the post-pandemic where many died as a result of the worsening of collateral diseases caused by the coronavirus, we expected more solidarity and respect for human life.
we expected some positive reaction from humanity in the post-pandemic where many died as a result of the worsening of collateral diseases caused by the coronavirus, we expected more solidarity and respect for human life.
Ukraine will start the year with a day of mourning due to the massive attack carried out by Russia that killed 39 people and injured 159 others, most of them civilians, the UN declared the attack “unacceptable” and the United States admits direct intervention in war through its troops, this would in practice represent the beginning of a 3rd. World War.
In addition to this crisis, there is the scourge of war in the Gaza strip and tension between Venezuela and Guyana.
The year is not yet over and this month the blog broke its record number of hits with more than 32 thousand and the new line where we delve deeper into the issue of the noosphere, based on Teilhard Chardin who coined the term, also the crisis of thought (we see that the philosophy is also experiencing a crisis) and which is the origin of the current civilizational crisis and Cyberculture, with ethical and social aspects that are deepened in readings of both the emergence of new technologies (ChatGPT, Bard, Azure, etc.) that enter the Era of Generative AI, in the LLM (Large Language Model) model.
The complex scenario requires reading a few authors who detect the golden thread of the current crisis, the idealistic model that comes from the dualism of Ancient Greece (being is and non-being is not), the centralizing and monopolizing state model (even the liberal model that grows in some countries continues to dictate centralized theories and models) and whose crisis affects the social body, culture and even religion where there is no shortage of false prophets, soothsayers and apocalypticists, this appeal grows depending on the severity of the time.
We leave a breath of hope, of certainty that it is possible to emerge from a crisis with balance, responsibility and a dispassionate look at problems, passion for life yes, but not that of fanatics and saviors of the country who contribute little or nothing to humanitarian and responsible for the human future.
Confidence and humility
In moral philosophy there are two types of trust: trust, which is characterized by the deepest interpersonal relationship, which involves good will and vulnerability, and reliability, a more basic type of trust that refers to the functioning of the world and things.
trust, which is characterized by the deepest interpersonal relationship, which involves good will and vulnerability, and reliability, a more basic type of trust that refers to the functioning of the world and things.
A good interpersonal relationship cannot be established without respect, and respect requires humility, simplicity and true relationships. Reliability also involves humility in learning how the world and things work and finding balance in social relationships.
There is an epistemological concept that works on the issue of trust, it involves testimony, it helps knowledge both in personal relationships and in reliability.
Interpersonal conceptions propose a use of the concept of trust based on analogies, and can be applied to epistemological debates without neglecting the moral issue.
This neglect due to an excessively objective and even positivist conception that still strongly influences epistemic approaches is common. An interesting proposal to be analyzed is from Richard Foley (2001).
The use of moral concepts in epistemology (LOCKE, 1975; CHISHOLM, 1966) worked in moral philosophy to resolve epistemic questions, but it is questionable whether the simple reduction of epistemic concepts to moral is valid, Firth (1978) defends the irreducibility of epistemic concepts , saying that although they can be conceived in an analogous way, and may even be similar, they are not irreducible to each other, which can cause theoretical confusion.
So because they are analogous and relevant, because many of our daily beliefs (not necessarily objectively scientific concepts) are acquired by the speech acts of other human beings in everyday relationships, the problem then is precisely knowing how to accept these speech acts as epistemic sources, as they are in different cultures and on a large social scale.
Foley uses the concept of self-trust, but the relationship we establish with our own faculties is a relationship of reliability. If we look for the origins of both concepts, we will find considerable differences between rely and trust, but they are used as synonyms and ignore the differences.
Foley’s mistake is precisely because he disregards the moral characteristics of trust, and it is important to be studied because of this, in everyday life we forget that trust involves moral aspects, including a fundamental one, which is humility in recognizing the speech of the Other.
CHISHOLM, R. (1966) Theory of knowledge. Englewood Cliffs: Prentice-Hall.
FIRTH, R. (1978) Are epistemic concepts reducible to ethical concepts? In: GOLDMAN, A. I.; KIM, J. Values and Morals. Dordrecht: D. Reidel.
FOLEY, R. (2001) Intellectual trust in oneself and others. Cambridge, New York: Cambridge University Press.
LOCKE, J. (1975) An essay concerning human understanding. Oxford: Clarendon Press.

