
Posts Tagged ‘smart city’
The Falling Virus as New Concerns
The number of cases in Russia that remained high, new cases emerging in China attributed to the Delta variant, according to data from the country’s own National Health Commission, accused 32 cases in Inner Mongolia, in the north of the country and which has already spread throughout In 11 provinces, cases have been confirmed in Guizhou in the South, Shandong in the East and in Gansu near Inner Mongolia, three cases in Beijing and two in Yinshou, in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region.
emerging in China attributed to the Delta variant, according to data from the country’s own National Health Commission, accused 32 cases in Inner Mongolia, in the north of the country and which has already spread throughout In 11 provinces, cases have been confirmed in Guizhou in the South, Shandong in the East and in Gansu near Inner Mongolia, three cases in Beijing and two in Yinshou, in the Ningxia Hui Autonomous Region.
In Brazil the moving average of deaths continues to fall, now in the range of 260 deaths, with 75% having already taken the first dose, and 55% the necessary doses, it is possible to predict a Christmas and a milder end of the year of the Pandemic in the country, many collective events are already released, games with 100% of the fans and parties and public shows.
The concern now turns to social problems arising from the pandemic, unemployment, impoverishment and rising prices. Even if some social aid does come, it will be insufficient to contain the spread of the crisis.
The closing of downtown offices, the mandatory use of masks and the restrictions imposed on restaurants have transformed landscapes into cities around the world, and are likely to continue in the long term, such as rethinking urban space, what to do with office buildings , closed stores and restaurants in the city centers, smart cities showed paths with a trend, apparently only electronic, now it seems inevitable, in Singapore even policing is done by robots (photo).
The immense empty spaces must be preserved and cared for, without robots the cost is high for a small population, so in many cities they will either remain abandoned centers or they will have to develop more computerized forms of maintenance and policing, in addition to the existing cameras.
It is likely that a reasonable number of people return to the routine of agglomerations in large centers, but there is a tendency to go to smaller cities or leave urban centers and work at home.
The future and our life in 2100
We have written a few posts about Michio Kaku, about some of his speculations about physics, now we want to give him a jump in the future, different from what the technoprofetas do (the name given by Jean Gabriel Ganascia to the creators of technological myths), Kaku speculates using physics and being optimistic.
now we want to give him a jump in the future, different from what the technoprofetas do (the name given by Jean Gabriel Ganascia to the creators of technological myths), Kaku speculates using physics and being optimistic.
He writes: “In 2100 our destiny is to become like the gods we once worshiped and feared. But our tools will not be like magic wands and potions, but computer science, nanotechnology, artificial intelligence, biotechnology and, above all, quantum theory, which is the basis of earlier technologies. “(Kaku, 2011)
If positioning as a quantum physicist, the term is inappropriate but would say theoretical, he asks: “But where is all this leading technological change? Where is the final destination of this long journey in science and technology? “.
His answer is surprising. It responds in a sociological way: “the culmination of all these disorders is the formation of a planetary civilization, what physicists call Type I civilization,”
Not surprising to those who connect all Newtonian mechanics with the logic that lasts until our days to the right, economic ideas and theories of the state.
And he goes on: “Unless we succumb to the forces of chaos and madness, the transition to a planetary civilization is inevitable, the end product of the enormous, inexorable force of history and technology beyond any control.”
Futurists already anticipated the office without paper, but the bureaucratic chaos makes the paper still to be spent exorbitantly, the work at home is not yet reality, but it could be.
Also the online shopping cybershoppers, cyberstudents making classrooms obsolete, and many universities would close due to lack of interest from young people.
What we see is proliferating cyberclassrooms and universities still record record numbers of students, professors who successfully give lectures on philosophy, physics and technological gadgets, giant media puzzles try to manipulate people’s heads, but “the lights of Broadway shine still as intensely as before. ”
But technology continues to be fought as one of the “evils of our time,” and according to Kaku the point is: “Whenever there is conflict between modern technology and the desires of our primitive ancestors, these primitive desires gain more and more.” : “This is the cave man principle”.
Kaku tells a story similar to today, watched a movie that changed his life was the “Forbidden Planet,” based on Shakespeare’s play “The Storm” in the movie astronauts find an ancient civilization but millions of years our front.
The discovery of the Chauvet Cave in southern France, where we rediscover primitive man capable of an art and a subjectivity comparable to our time, is nothing more than the idea of this Cave Man who subsists in us and insists on not going to the future.
The book does not end there, his belief in the future is strong and resilient, but one sentence of Schopenhauer translates well his vision: “Each one limit the world’s limits in his vision,” personally he would add but the limits are greater than our vision.
Kaku, M. (2011) Physics of the futuro: how science will shape human Destiny and our daily lives by the year 2100.
e-Estonia: a digital country
Since its independence from the former Soviet Union (20 August 1991),  Estonia decided it would be a country that would remain connected, decentralized, on an open platform infrastructure and a continuous process to keep improving, calling it four principles in its site.
Estonia decided it would be a country that would remain connected, decentralized, on an open platform infrastructure and a continuous process to keep improving, calling it four principles in its site.
The two key points of this e-citizenship is the identity card or e-ID and decentralized connection called infrastructure X-Road, they open the door to all state services, social and economic data, and the eID identification able to verify the identity of a person around the online environment.
The people of Estonia are the source of the Phoenicians, but are intimate and ethnically related to Finnish and Sami (northern Norway), so with historical links to all of Scandinavia, and the port of Tallinn as its capital and largest city, with the all over the country about 1 million and a half inhabitants.
With this economy has benefited from the strength of the electronics and telecommunications sectors and strong trade ties with Finland, Sweden, Russia and Germany.
The system of government is parliamentary with a Congress of 101 deputies elected directly by the vote of the citizens.
Estonia joined the European Union on 1 May 2004, while Latvia and Lithuania, has a GDP of US $ 35,398, which gives a per capita income of $ 26,000.
(Português) Infraestrutura nas cidades
Among the items analyzed by IBEU, although sanitation is a priority, most notably  among negative aspects is the urban infrastructure (sidewalks, paving, street lighting, etc.) as 91.5% are in bad levels and very bad , corresponding to 2,579 as bad (46.3%) and very bad (45.2%), ie, the issue is very serious.
among negative aspects is the urban infrastructure (sidewalks, paving, street lighting, etc.) as 91.5% are in bad levels and very bad , corresponding to 2,579 as bad (46.3%) and very bad (45.2%), ie, the issue is very serious.
The data shows that are great urban problems of Brazilian municipalities. Perhaps the main is the urban infrastructure (paving, sidewalks, street lighting etc.), as 91.5% of the municipalities are in bad and very bad levels, corresponding to 2,579 as bad, and 2,516 as very bad.
Among the capitals, those with good to average conditions are: Victoria (1), Goiania (2), Rio de Janeiro (3) São Paulo (4), Curitiba (5), Belo Horizonte (6), Brasilia (7) , Porto Alegre (8) and Florianópolis (9), are in poor condition: Aracaju, Campo Grande, Palmas, Recife, Salvador, Fortaleza, Teresina, Manaus, Natal, Cuiabá, João Pessoa, São Luís, Maceió and Bethlehem, and very bad conditions: Rio Branco (24), Boa Vista (25), Porto Velho (26) and Macapá (27).
There are only 441 municipalities in average conditions of well-being as urban infrastructure, 28 have good conditions, and only one in very good condition that is Camboriú (SC).
The map shows small regions between light yellow and blue mean the conditions is average and good, while shades of red indicate the poor and very poor conditions.
Smart-cities no just technologies
 The answer is of course not, according to the website of BBC News, the question is not easy to answer, but finding intelligent form of relieving congestion and pollution, using sensors and data, means a way to push smart cities (smart cities) and also make the greenest cities with more parts, and bike-sharing measures are intelligent.
The answer is of course not, according to the website of BBC News, the question is not easy to answer, but finding intelligent form of relieving congestion and pollution, using sensors and data, means a way to push smart cities (smart cities) and also make the greenest cities with more parts, and bike-sharing measures are intelligent.
There are already several smart cities around the world, as the cities of Songdo in South Korea, which have high technology across their infrastructure and green city Masdar in the United Arab Emirates, but there are other creative solutions.
You can also find slums as Stellenbosch, Cape Town, where the houses are powered by solar panels and this is replaced by cellular refills as award for energy savings.
The Inglatera awarded the city of Glasgow with 24 million pounds, for being chosen as the city most applicable technologies for smart cities in the UK, which hosts the Commonwealth Games, but it also has its social problems, for example, lower life expectancy in the UK.
The city however is applying part of the earned money to solve the problem life expectancy, using data from the big date, she wants to solve the problem which is known also with the name of Glasgow City, that within seven kilometers of the city the expectation reduces life of 28 years, which is dramatic.
But the city has solved the problem of energy efficiency in urban areas, and people spend a smaller amount of household income on fuel, provides a privileged urban routing for public transportation in areas that were underserved.
City Recife has featured as a digital city
Recife had his Porto Digital launched in 2000 , especially in the magazines Wired and Bloomberg now has featured on BBC News, which still states that ” large international companies not met in Recife , but the steady growth of the hub … can be a salutary lesson . ”
After 13 years exporting products and services to the world , the center still has to overcome a barrier no amount of internet connections high speed can overcome , and according to the BBC News also geography .
The website of the British newspaper states that the distance between north and south remains, but that these investments can break this logic .
Now some technology companies in the Porto Digital , are opening offices in São Paulo as a way to expand, but to be the southern branch means that they will be commercially viable ( and available ) to potential customers , which still tend to be a little suspicious companies based Recife , explains the news .
Also according to the newspaper, Sergio Cavalcante , CEO of the Center for Recife Studies and 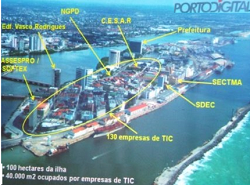 Advanced Systems said : ” Truth be told , our market is not yet in Recife , not in our northern region’s in Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and abroad. We are sending our CEOs to São Paulo , in fact , but our 200 companies are developing and headquartered here in Recife . they are based here , “said the CEO of the company established in 1996, which is the largest business in the digital port .
Advanced Systems said : ” Truth be told , our market is not yet in Recife , not in our northern region’s in Sao Paulo, Rio de Janeiro and abroad. We are sending our CEOs to São Paulo , in fact , but our 200 companies are developing and headquartered here in Recife . they are based here , “said the CEO of the company established in 1996, which is the largest business in the digital port .
The highlight of the Porto Digital Reef can be an inspiration for future regional disparities and national development prospects, which is not only agrarian.
Mobilidade urbana, calçadas e aplicativos
Mobilidade urbana é o tema de grandes cidades, a solução pensada para São Paulo por diversos governos,  já eram soluções conhecidas em Kuala Lumpur e também em Las Vegas (veja as fotos).
já eram soluções conhecidas em Kuala Lumpur e também em Las Vegas (veja as fotos).
Quem trafega pela Av. Roberto Marinho em São Paulo observa que a execução as obras da Linha 17-Ouro está parada e somente há vigas no meio da via e canteiros de obras ao centro, a outra linha prioritária para a cidade que é a Linha Prata, terá 24,3 quilômetros, ligando a Vila Prudente a Cidade Tiradentes, o trecho que é uma extensão e era chamado de linha verde tem as obras atrasadas.
O único trecho previsto para ser entregue até a Copa do Mundo é o de menos de 3 km, ligando a Vila Prudente a Oratório, cuja previsão de entrar em operação é a partir de dezembro de 2013.
Certos que não realizaram as “promessas” para a Copa do Mundo, agora discutem as calçadas, que são também importantes, mas só farão sentido se o transporte de massa estiver resolvido, e não está. As vias de bicicletas também são importantes !
Certos de que continuaremos por algum tempo neuróticos com o transporte urbano, obrigados a trafegar de carro, precisamos aproveitar para dar carona, vejam o site caroneiros.com e usar aplicativos para saber por onde podemos “fugir” para tentar chegar em casa, um aplicativo onde os usuários das vias públicas se comunicam é o Waze.com .
Por enquanto não vamos ganhar nem ouro nem prata.
Um planejamento urbano novo
 Temos postado em diversos posts sobre Smart Cities, cidades inteligentes que alguém mal avisado pode imaginar que seja apenas uma cidade ecológica ou digital, que é um aspecto relevante, mas existem outros: sociabilidade, segurança, transportes, etc.
Temos postado em diversos posts sobre Smart Cities, cidades inteligentes que alguém mal avisado pode imaginar que seja apenas uma cidade ecológica ou digital, que é um aspecto relevante, mas existem outros: sociabilidade, segurança, transportes, etc.
Agora pesquisadores portugueses (Jorge Pacheco e Francisco C. Santos)desenvolveram uma ferramenta matemática para investigar fatores de planejamento urbano que são essenciais, e classificaram os padrões de desenvolvimento em cinco tipos, com características previsíveis e comportamento que exigem diferentes intervenções e medidas políticas, mas infelizmente é ainda só um relatório científico.
A lógica que existe por trás de selvas de cimento de nossas cidades comportam-se como organismos vivos do qual participam governantes, mas também indivíduos, por isto é necessário uma análise ao longo do tempo, e não apenas em períodos exatos.
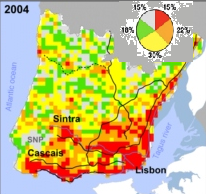
Os pesquisadores se fundamentaram seus estudos na “grande” Lisboa (MAL, Metropolitan Area of Lisbon), que teve 3 etapas distintas, nos anos de 1960, 1990 e 2004, e foram desenvolvidos não apenas em níveis de construção, mas principalmente em áreas distribuídas na superfície, densidades e fragmentações como padrões espaciais da cidade e variações no tempo, conforme divulgou a Ciência Hoje.
A partir de dados sobre MAL urbanização três anos diferentes – 1960, 1990 e 2004 – que desenvolvem uma classificação matemática baseada não apenas em níveis construídas, mas também sobre como essas áreas são distribuídas na superfície e como densa ou fragmentado é o padrão espacial da cidade, bem como a forma como estes variam com o tempo.
O interessante é que entre os cinco tipos (na figura em cores: branco, amarelo, verde, alaranjado e vermleho), onde há tipos bastante previsíveis e outros caóticos, com espaços perto da saturação, ou espaços onde construções são raras.
Dois tipos chamados de 3 e 4 são de interesse real, com terras livres para construção, mas que a distribuição pode ter alta variações quando as formas de construção são organizadas e quais podem ser colocadas em crescimento descontrolado e caótico.

